Today, geographic information analysis is among the most powerful tools for businesses and cities. Almost everything is location-based: where customers are, how transport moves, where the risk of flooding is higher, or even where it's best to put up a billboard.
Spatial data analysis helps insurance companies assess risks, logisticians build routes, and farmers monitor crops. This article will consider what this analysis is, how it works, which industries require it most, and how it can change the future.
What Is Geospatial Data Analysis?
Geographic information analysis is a way of studying data about location. Based on the coordinates of objects, geo-analytics allows businesses to determine dependencies between these objects and get valuable insights. Let's look at this more simply. Imagine that you have more than a list of addresses or coordinates – a whole map showing what is happening, where, and why.
What is geospatial analytics, with examples? For instance, if you own a chain of stores, spatial data analysis will help you understand where your target audience lives and which areas bring in more profit. So, you determine where it is worth opening a new store and developing your business venture. If you work in logistics, location-based analysis will help to build routes faster and cheaper.

In essence, spatial data analysis combines maps, data, and analytics. It helps find patterns, predict events, and make more accurate decisions while considering where all these activities (pattern finding, prediction, decision-making) happen geographically.
Spatial data analysis is used in marketing, logistics, medicine, agriculture, and other fields. Understanding what and where it is happening is essential for all business sectors.
How Geospatial Analysis Works
Location-based analysis starts with data gathering, but a technological process is needed to make that data useful. Let's consider how the data transforms into actionable insights, step by step:
Data collection and processing
Such data comes from many sources: satellites and drones, GPS trackers, city sensors, and mobile applications.
-
Satellites and drones: Provide high-resolution images, often in real-time;
-
IoT sensors and weather stations: Record data on weather, humidity, temperature, water level, movement, and more;
-
GPS devices and mobile phones: Allow tracking of the movements of people, vehicles, and goods;
-
Mapping services and databases (OpenStreetMap): Provide data about infrastructure, roads, buildings, etc.
We can group location-based data in raster and vector forms.
-
Raster form: images made of pixels (heat maps, aerial photos);
-
Vector form: shapes and points with attributes (points - location of a tree or bus stop, lines - roads, rivers, polygons - building footprints, country borders).
However, for all this data to start working, the information must first be put in order. It should be structured, synchronized, and converted to a single coordinate system. However, before it, we need to preprocess the obtained data, which means the following:
- Errors, noise, and duplicates should be removed;
- Coordinates should be converted to a single system (for example, WGS 84);
- Data from different sources needs to be synchronized in time and space;
- The metadata should be added (time of shooting, source, update frequency).
Data processing uses specialized programs and GIS platforms like ArcGIS, QGIS, or PostGIS.
Below is an example of integrating spatial data layers in GIS for analysis and output visualization.

Data visualization
Once the data is processed, it becomes a visual tool. There are different types of geospatial analysis visualization: maps, diagrams, and interactive panels. For example, a heat map could show which parts of the city sales most often occur or where most people gather at a certain time of day. Based on current trends, it could also be a traffic prediction map demonstrating where traffic congestion is expected in a week.
Here are the most common types of geospatial visualizations:
-
Thematic maps: Show, for example, population density, noise level, or product prevalence;
-
Heatmaps: Visualize concentrations - people, events, purchases;
-
Interactive panels (dashboards): Allow filtering of data by time, location, and indicators;
-
3D models: Used for urban modeling or development assessment.
Such visualization helps experts immediately see patterns that may not be noticeable in tables.
Find out how industry leaders are applying generative AI in logistics
Algorithms and AI
The true power of geospatial analysis becomes clear when artificial intelligence and machine learning are involved. Geospatial models with AI algorithms can analyze complex scenarios, such as how store availability will change if one of the roads is closed.
With machine learning, even deeper capabilities appear. Based on historical data, the system can predict where demand will soon begin to fall or where the risk of flooding will increase.
Data interpretation and action
The result of the entire process of location-based analysis is insights that can be applied in practice. These practical insights are used in areas such as:
-
Marketing: companies can find out where the target audience lives and how best to communicate with them;
-
Logistics: enterprises get insights on how to optimize delivery and reduce costs;
-
Risk management: It is possible to understand where failures, accidents, or overloads may happen.
Geoanalysis allows businesses to react to problems, anticipate them, optimize processes, and act more accurately.
What is especially important when applying location-based analysis is that all data becomes visible, not in raw numbers but on a map in a real context. It means that decisions are not made blindly but based on a clear understanding of the real-world situation.
Business Applications of Spatial Data Analytics Across Industries
CIO, a leading resource for Chief Information Officers, reports that about 80% of companies have location data. Enterprises need this data, including addresses and zip codes, to run their businesses effectively.
Geoanalytics helps enterprises better understand and optimize their operations. Let's consider which industries benefit most from geographic information analysis.
Insurance & real estate
Companies in this sector use spatial data analysis to assess real estate remotely. Drones can inspect the structural condition of a home and the roof and help identify nearby risks. For example, rivers can cause floods, and forests can increase wildfire risk. Geospatial analysis speeds up underwriting, assessing risks, and calculating insurance premiums.
Marketing & advertising
Brands use geosegmentation to divide the target audience by districts, streets, or even buildings. For example, a fast-food restaurant can launch ads only for people who work nearby. Geoanalytics also helps choose locations for outdoor advertising. Marketers analyze where the highest traffic is and place billboards where the right people will see them.
Logistics & transportation
Companies use geoanalytics to plan optimal routes, considering traffic jams, weather conditions, and time of day. Logistic companies can also analyze transport accessibility: how long it takes to get to a warehouse, client, or pick-up point. With this information, companies can reduce costs and speed up delivery.
At Requestum, we know how to create software with integrated geospatial data processing capabilities. One of our cases is the implementation of a demand forecasting solution for transportation services. It can forecast demand for transport in different areas of the city. The predictions are based on analyzing population density, points of interest, and user behavior.
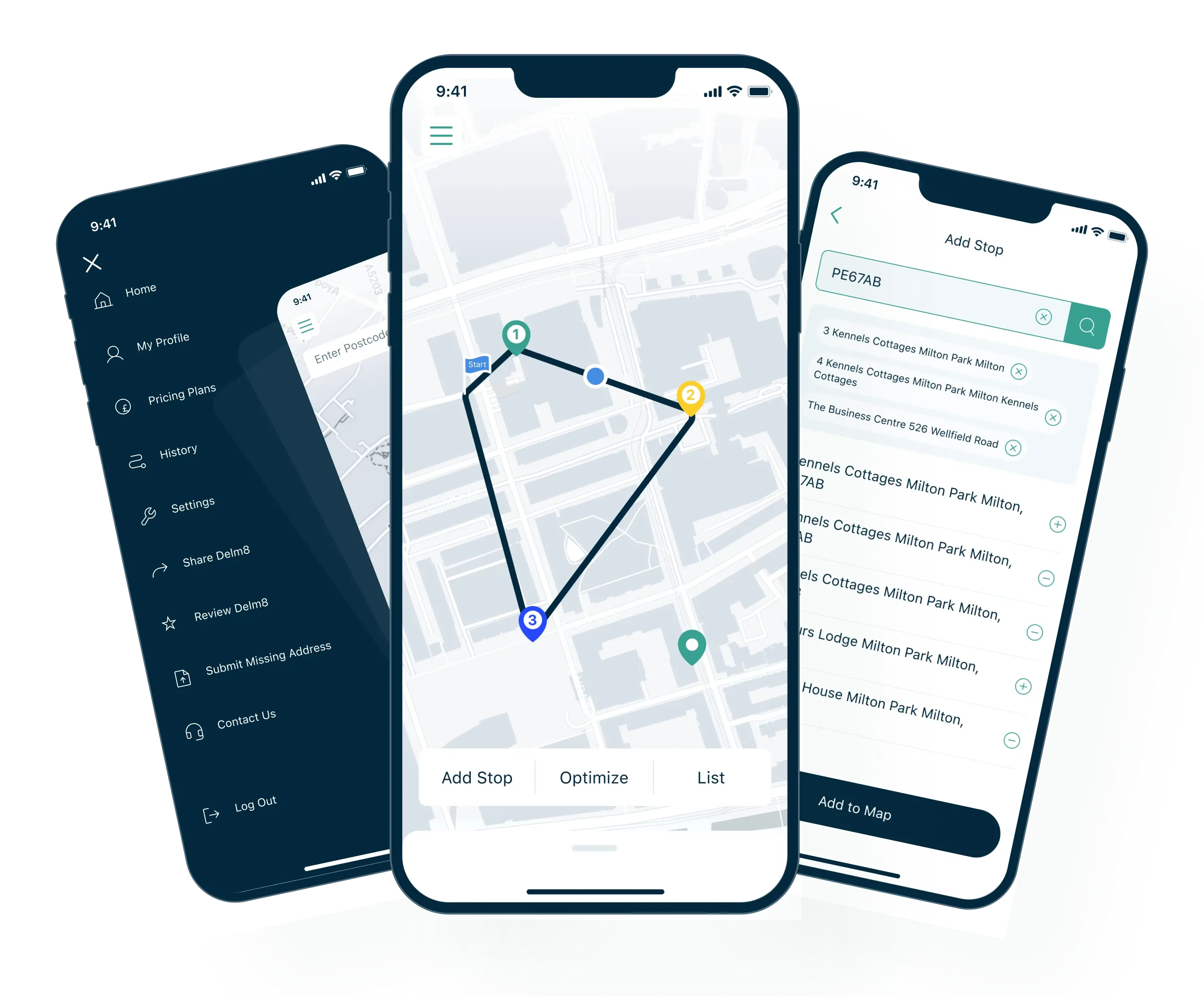
Case Study: Effective Navigation Solution for UK-based Drivers
Agriculture
Farmers use geoanalytics to monitor the condition of fields. Drone and satellite images show which areas are suffering from drought and where pests or plant diseases have appeared. This data helps optimize irrigation and fertilizer distribution and predict crop yields.
Public health
Location-based analysis can be used during epidemics to show where infection hotspots are formed. It helps healthcare organizations identify risk zones and prepare in advance. For example, organizations can send vaccines to certain areas to prevent a real explosion of infection.
Urban planning & sustainability
Satellite geospatial analysis helps cities manage infrastructural growth and divide the urban area into zones (zoning). Governments can understand where there is a lack of infrastructure, schools, hospitals, and parks. It helps create cities with convenient routes, green areas, and comfortable living environments. For example, if new residential buildings appear in an area, governments understand there is a need to build bus stops or clinics.
One of the software solutions we created is designed for the detection of cars on overhead images. It is software that can identify car density in certain city areas using an object detection system and map visualization. This project aims to provide information about car traffic and help with urban planning through spatial pattern analysis.

Why Geospatial Analysis Matters for Business
Geographic information analysis helps businesses see patterns, optimize operations, make smarter decisions, and save resources. In this section, you will discover why businesses need this analysis in the modern world.
Making more informed, data-driven decisions
When a business owner chooses where to invest, launch a new product, or open an office, it often has to rely on intuition, old reports, or average figures. Location-based analysis changes this approach: it allows entrepreneurs to see a direct connection between location and result.
For example, a delivery company may find that some areas consistently cause delays due to logistical dead ends. So the firm can optimize routes without increasing costs.
Reducing costs and increasing operational efficiency
A business does not always need to make big changes to get results. Sometimes, just understanding where inefficiencies occur can make a difference.
Geoanalysis helps identify such bottlenecks. These can be warehouses located too far from customers, locations with low foot traffic, or routes where couriers spend more time than necessary.
Suppose a company receives data on the weather, traffic jams, or even seasonal flows of people (for example, in the summer, they leave the center for the suburbs). In that case, it is possible to optimize processes further.
Understanding customers in a real context
Many companies know their customers pretty well. They know their age, gender, and income. However, not every business understands where these customers live, work, move, and what they stumble upon on their way home.
Geoanalytics allows businesses to see people in their real, physical environment, enabling them to build more accurate and actionable strategies.
For example, if a business owner notices that most customers come from the southwestern part of the city, they might consider opening a branch closer to them.
Seeing the Unseen: Future Trends in Geospatial Analytics
Geoanalytics is already capable of impressive things, but the most exciting trends are yet to come.
Real-time spatial data streams
Previously, getting spatial data involved delays. Experts had to wait until the data was gathered, processed, and uploaded. That's no longer the case. Data can be obtained and analyzed immediately thanks to sensors, cameras, GPS, and smartphones.
Real-time geospatial data is already being used in smart cities and emergency services - its role will only grow. For example, in response to wildfires in California, GIS tools helped map hot spots, manage resources, and monitor fire crews, allowing for faster decisions.
Augmented reality and immersive maps
Now, businesses use augmented reality even more to show what a building will look like before construction begins or how best to arrange store shelves.
Imagine you're not just looking at a map from above - you're walking through the city, seeing buildings, people, and transport and all this in real-time. It is what AR map creation startups are doing.
Google Maps has already integrated AR into its navigation system. So, pedestrians can receive real-time directions superimposed on the image from their smartphone camera.
Deep integration with AI and ML
Artificial intelligence already helps uncover hidden patterns in geodata. But there's more to come. Even today, neural networks can predict where flooding is possible or how cities will grow.
AI algorithms learn from a huge array of data and help create not just maps but scenarios for the future. It is used, for example, in environmental monitoring and climate risk mitigation.

Scalable SaaS and APIs for geospatial analysis
Previously, spatial data analysis was only available to large companies with servers and expensive GIS systems.
Today, cloud-based services make this accessible to everyone. There are ready-made APIs that allow experts to integrate maps, routes, and geoanalytics directly into apps. It opens up opportunities for small businesses to leverage geospatial data. It's like Google Maps but with additional features such as forecasts, coverage areas, and audience segmentation.
Software solutions such as Microsoft Azure Maps include map visualization, route building, traffic analysis, and geofencing. The platform integrates with other Azure services and allows you to build full-fledged business solutions without deploying infrastructure from scratch. We can expect to see even more such solutions emerge soon.
Let’s turn your idea into a working solution
Blockchain & geospatial data analytics
Combining blockchain with GIS opens new ways to make spatial data more secure and reliable. The global blockchain market is expected to grow rapidly, at more than 87% per year. Specialists suggest it could reach 1,431.54 billion by 2030.
Blockchain is not just about cryptocurrency. This technology helps verify the accuracy and transparency of geospatial data. For example, real estate platforms use it to simplify property purchases by offering a secure and open record of every transaction.
Conclusion
Geospatial analytics helps companies understand data through location and improve their business operations. Spatial data analysis shows not only what is happening but also where. Thus, business owners can make more accurate and informed decisions.
This technology is already making a real difference in logistics, retail, real estate, agribusiness, marketing, and city management. Key benefits are cost optimization, a better understanding of customer behavior, and the ability to predict risks and demand.
Looking ahead, there's even more to come: real-time analytics, 3D maps, AI integration, and cloud platforms that make geoanalytics accessible and scalable. If you are thinking about using geoanalytics in your project, contact us. We'll help you turn spatial data into real business value.

Our team is dedicated to delivering high-quality services and achieving results that exceed clients' expectations. Let’s discuss how we can help your business succeed.




SHARE: