Generative AI is an impressive leap in technology. It takes inputs, learns from them, and then spits out completely new creations. It is changing how tasks are executed in various sectors, with logistics being a prime example. By learning from logistical data, AI can produce innovative solutions for organizing and streamlining supply chains. This technology's capabilities are transformative, from forecasting demands to developing smarter delivery routes. This article looks at how generative AI in logistics transforms the sector and reveals new possibilities for businesses. We will provide examples of operational improvements and even touch on potential future advancements in this field.
Understanding Generative AI
Generative AI, a subset of artificial intelligence, stands apart for its ability to interpret data and use it to create something new. Traditional AI systems might analyze data and provide insights, whereas generative models take this a step further. They learn from patterns in the data they're fed, whether text, images, or numerical datasets, and then generate original, predictive outputs. This capability makes them suited for tasks where innovation or forecasting is key.
Generative AI's potential becomes even more intriguing when considering its capacity for innovation. In any sector where forecasting or simulating different outcomes is crucial, it can provide a range of possibilities, not just extrapolate on existing trends. For example, it can design novel chemical compounds in pharmaceuticals or create multiple architectural designs that meet specific criteria in construction.
The defining feature of generative AI is its foresight. It goes beyond reacting to what will happen, venturing into what could happen. With the right data, it can simulate outcomes and offer a sandbox for experts to explore potential futures.
Implications of Generative AI in Logistics
Introducing Generative AI into the logistics sector could herald a new era of efficiency and strategic planning. Here's how it could transform the industry.
Route optimization
By analyzing traffic data, weather reports, and historical transit times, generative AI can devise the most efficient routes for delivery, which can reduce fuel consumption and guarantee timely arrivals.
Learn how GPUs tackle complex routing challenges
Demand forecasting
It can anticipate market demand, which allows companies to adjust their inventory and staffing levels accordingly. It will reduce waste and improve customer service.
Maintenance scheduling
Generative AI can predict when equipment or vehicles will likely need maintenance, preventing breakdowns before they occur and avoiding costly delays.
Supplier selection
By assessing cost, reliability, and quality, the AI can assist in selecting the best suppliers, reducing risk, and improving supply chain resilience.
Pricing strategies
It can generate dynamic pricing models based on supply and demand dynamics, competitor pricing, and market conditions.
The abovementioned capabilities show generative AI's potential to streamline logistics operations and make them more adaptable, predictive, and efficient. These improvements can lead to reduced operational costs, enhanced customer satisfaction, and a more robust bottom line for logistics companies.
Transportation and Routing Optimization within Supply Chain Management
In the supply chain management domain, the strategic planning of transportation and routing plays a critical role. The introduction of generative AI in the supply chain has allowed it to analyze large datasets and generate transportation plans that enhance time management and overall supply chain performance.
It starts by pooling data from numerous sources, including traffic reports, weather conditions, vehicle performance, and delivery schedules. This data forms the basis of a complex analysis, where the AI identifies patterns that influence delivery times and efficiency. Then, the AI develops a series of potential routes. It evaluates each based on several factors, such as the shortest distance, anticipated traffic, and prevailing weather conditions.
As the AI receives feedback from the real-world outcomes of its suggested routes, it fine-tunes its algorithms so that subsequent recommendations are even more accurate. Generative AI contributes to a more sustainable supply chain. Efficient routing translates to reduced fuel consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions – it helps companies save on operational costs and progress toward their sustainability goals.
The predictive capabilities of generative AI are a boon for anticipating and mitigating potential disruptions. It assesses risk by analyzing data trends, such as the impact of seasonal changes on shipping routes or the likelihood of delays at certain ports. These insights allow logistics planners to adjust their strategies and save time by avoiding potential bottlenecks.
Case Study: Real-Time Asset Visualization Tool
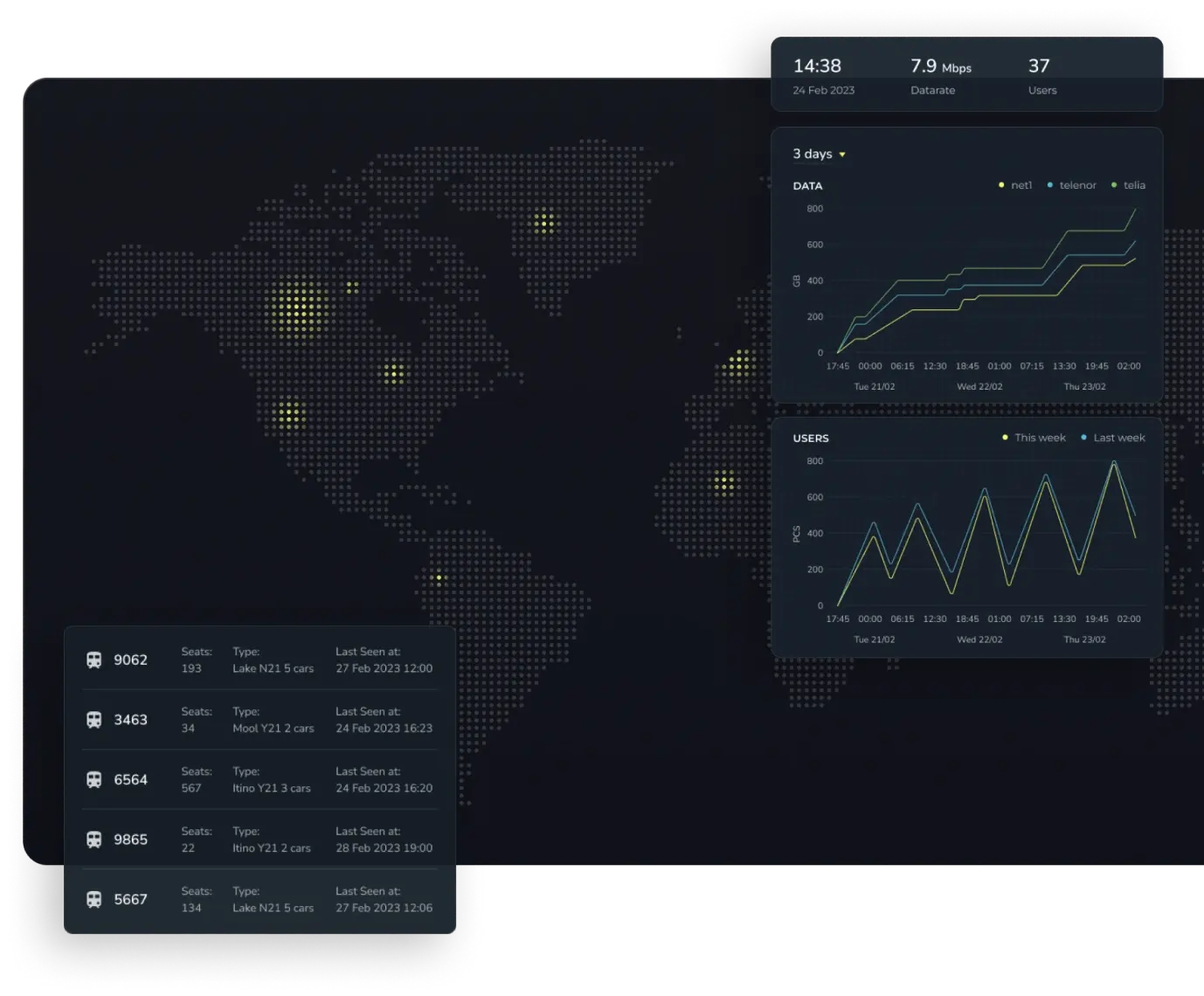
Streamlining Warehouse Operations
Generative AI plays a transformative role in the efficiency of warehouse operations by tackling one of the industry's greatest challenges: bottlenecks. The technology applies its data-crunching prowess to warehouse logistics and generates plans that provide a smoother flow of operations.
Here's how generative AI brings innovation to the warehouse floor:
- Layout optimization. It analyzes historical movement data to propose designs that streamline the flow of goods, reducing unnecessary movement and handling.
- Inventory management. Generative AI predicts demand patterns, suggesting stock levels that prevent excess and shortages.
- Task prioritization. It reviews order histories and current demands to sequence tasks to maximize productivity and minimize delays.
- Loading and unloading schedules. Generative AI crafts schedules that balance dock use so trucks load and unload with minimal wait time.
- Equipment deployment. It determines the optimal use of machinery like forklifts so they are available where and when the need is greatest.
By integrating these suggestions into their operational framework, warehouses can experience a reduction in hold-ups and increase throughput. Logistics planners receive summaries from the AI that distill complex data into actionable insights, allowing for quick and informed decision-making. Similarly, warehouse operators benefit from real-time updates that guide their day-to-day actions and allow them to focus on productivity without the guesswork.
Demand Forecasting and Eco-friendly Solutions
Generative AI's capabilities extend to demand forecasting, which processes historical sales data, market trends, consumer behavior, and external factors such as economic indicators to predict future product demand. This advanced forecasting supports businesses in maintaining optimal inventory levels, reducing waste, and ensuring product availability.
In eco-friendly logistics solutions, generative AI plays a critical role in several areas:
- Reduction in energy use. It forecasts energy needs for various logistics processes, suggesting the most efficient use of resources and contributing to a lower carbon footprint.
- Waste minimization. The AI predicts which goods will have higher turnover rates, which helps to reduce overproduction and minimize waste.
- Material recycling. It identifies the most efficient recycling pathways for materials and guarantees sustainable use of resources.
- Optimal product lifecycle. Generative AI aids in designing products with sustainability in mind. It contributes to the creation of goods that are durable, repairable, and recyclable.
Through these applications, AI not only streamlines operations but also fosters sustainability in logistics. It equips businesses to make smarter choices that benefit their bottom line and the environment.
Real-world Examples
Several forward-thinking companies have already used Generative AI to revamp their logistics and supply chain operations. Below are several examples that illustrate the capabilities in this sector.
Amazon
Amazon deploys generative AI to predict customer purchase trends, enabling a highly reactive inventory system that adjusts to demand while minimizing surplus stock. This application streamlines warehouse functioning and significantly curtails waste. AI-driven systems facilitate quick and precise package processing in sorting centers, further refining Amazon's delivery operations.
Procter & Gamble
Procter & Gamble (P&G) has turned to AI to fine-tune its demand forecasting. By digesting a wealth of historical sales data, weather patterns, and market dynamics, P&G's advanced AI models seek to predict consumer buying behaviors with heightened accuracy. This foresight allows P&G to calibrate its inventory to market needs, thereby minimizing excess stock and reducing operating costs.
Let’s solve your business challenges with innovative software
Flexport
Flexport integrates generative AI into its operations to bring unprecedented transparency and efficiency to shipping logistics. Its platform uses predictive analytics to arm clients with forecasts for inventory management, preparing them against potential supply chain disruptions. This predictive capacity means businesses can respond and adjust their strategies in response to global trade winds.
Llamasoft
Llamasoft offers a striking example of generative AI's potential in strategic planning. The company's technology simulates various supply chain scenarios, allowing businesses to foresee and prepare for disruptions. By modeling these scenarios, companies can pinpoint weaknesses in their supply chains, refine inventory distribution, and devise strategies that insulate them from future volatility.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the promise of generative AI's role in the logistics sector seems revolutionary, it comes with challenges and ethical considerations. Uncertainty surrounding regulation, potential misuse of technology, and initial implementation difficulties pose considerable challenges.
Here are some of the most pressing issues associated with adopting generative AI in logistics:
- Data privacy. Protecting sensitive information, such as operational data, supplier details, and customer data, from breaches is crucial. Generative AI systems must guarantee stringent data privacy protocols to maintain trust and compliance.
- Bias and fairness. It is essential to address inherent biases in historical data to prevent AI from perpetuating or amplifying them. It could lead to unfair practices or unequal service levels across different regions or customer groups without appropriate measures.
- Job displacement. As AI optimizes certain tasks, there is a risk that jobs, especially those involving routine planning and analysis, may be reduced. Companies need to manage this transition responsibly.
- Regulatory compliance. AI applications in logistics operate across international borders and must adhere to diverse data, transportation, labor laws, and regulations, which can be complex and varied.
- Security risks. There's a risk of AI systems being targeted by cyber-attacks. It could have far-reaching consequences on the supply chain. Security infrastructure needs to be a priority.
While these challenges hold significant consequences, they are not insurmountable. The key lies in robust governance and proactive risk management strategies. Equally critical is the ethical use of AI – it should augment human logistics capabilities rather than lead to unwarranted job displacement or inequality.
Conclusion
Generative AI in logistics and transportation promises to reshape the industry and provide new avenues for cost reduction and operational efficacy. Its potential is clear: smarter route planning, improved demand forecasting, and advanced decision-making processes. Yet, for the industry to embrace these advantages, addressing the attendant challenges with prudence and an ethical lens will be necessary. With careful navigation, the rewards of generative AI in logistics could be substantial and far-reaching.
Interested in harnessing the power of generative AI for your logistics and transportation needs? Reach out to us and take the first step towards transforming your operations with AI.

Our team is dedicated to delivering high-quality services and achieving results that exceed clients' expectations. Let’s discuss how we can help your business succeed.



SHARE: